Algorithm-Sorting
Data Structure: Set
Set Interface
Remember Data Structure is an interface, don’t do some dumb jobs… All you need to do is understanding the first principle of several data structures through practicing it.

If you use simply an array, it will cost time!
Data Structure Set
Lecture Notes from SJTU DS
Introduction
- 散列表:实现映射(集合提升性能的核心问题)
集合的定义
集合包含两个部分:键值和关键字值。
静态查找表
问题的定义:给定一个集合,需要查找关键字对应的元素是否存在。
从最基本的顺序查找()到对于有序集合的二分查找(),还可以进一步优化为插值查找,对于数据均匀分布的情况,可以进一步优化时间复杂度:
使用分块查找也可以进一步优化(详见分块思想)
- 为了最大化发挥分块的效率,我们需要对块内元素的性质做出规定:
- 例如,第块的元素一定大于第块的元素(并且建立索引表)
- 每个索引包括块内元素的最大值和该索引块的起始位置
- 这样就可以在多次查询的时候减少很多无效的比较,但是代价是需要额外空间储存索引并且在修改数组时需要更新维护这个索引表。
- 如果查找表很大,内存放不下,可以使用分块的思想高效的实现分块查找。
- 例如,第块的元素一定大于第块的元素(并且建立索引表)
STL 中的静态查找表
-
find():- 模版参数
- 迭代器类型
- 集合元素的类型
- 形式参数
- 两个迭代器对象(左闭右开)
- 需要查找的对象值
- 返回一个迭代器
- 模版参数
-
binary_search():使用二分查找的方式查找一个有序序列,返回是否存在
Sorting Algorithms
此处所有的排序算法都使用0-based。
Introduction
如何评价一个排序的好与坏?
-
排序的复杂度
- 时间复杂度:对数组排序所需要的时间开销。(最坏 & 平均)
- 空间复杂度:对应复杂排序函数的设计,往往需要额外的空间开销。
-
排序的稳定性:
- 稳定排序:对于关键字相同的元素的顺序不会变。
- 不稳定排序
-
排序的存储特性:
- 内排序:储存在内存
- 外排序:储存在外存
由于外存的设计导致其读取速度非常慢,我们放在下一章节《B和B+树》中详细讨论。今天讨论的排序算法都是针对在内存上连续空间的讨论。
根据排序的方式,我们主要可以分为以下的若干排序方式:
- 插入排序
- 直接插入排序
- 二分插入排序
- 希尔排序
- 选择排序
- 直接选择排序
- 堆排序
- 交换排序
- 冒泡排序
- 快速排序
- 归并排序
- 基数排序(桶排序)
Insert Sort
直接插入排序
类似于打扑克牌的插入过程,保持数组的有序性并不断在对应位置插入新的元素。
时间复杂度: (逆序是最坏的情况)
Code
1 | |
插入排序在原地移动就可以了,不需要使用额外的空间,对于外层循环,代表已经被排序好的区间,并对位的元素做插入操作。
复杂度分析
如果直接从代码角度分析,两个for循环嵌套直接,或者我们可以把这个过程abstract成若干个子过程:
- 找到需要被插入的位置。
- 执行插入操作。
二分插入排序
因为已排序的数组保证了有序性,因此可以在查找的过程中使用二分查找,比较的时间复杂度降为,但是插入的时候时间复杂度没有下降,总的时间复杂度还是
希尔排序
Intuition:避免大量的数据移动,使用交换来替代大批量的数据移动。
- 先比较离的远的元素(此时步长大,移动的效率高)
- 步长不断减小直到1
在直接插入排序的过程中,每插入一个新元素都需要进行线性的移动才可以插入到正确的位置,希尔排序的关键在于减少排序移动的次数,因此希尔排序从步长大的开始,交换元素(相当于做了很多次的移动)。希尔排序选择了一个序列,作为每一次的步长。
希尔排序的重要性质:一个有序的数组经过排序后仍然是有序,因此步长不断减小的排序逻辑是行之有效的!
最终希尔排序会执行一个的直接插入排序,看似时间复杂度不增反降,实际上,每一次排序都会接近于最好的情况,出现最坏情况的几率会少的多。
因此,希尔排序的关键在于希尔序列的设计,在这里我们选择了不断二分的希尔序列。
1 | |
Select Sort
选择排序:对于元素中不断取出最小的元素(或者最大的元素),与数组的未排序的部分的首元素交换,实现序列的重组。
Simple Select Sort
对于直接的选择排序,对于未排序的部分(一开始就是整个数组),找出元素中最小的值,和第一个元素的值做交换。接下来未排序的部分就成了,接下来在做相同的操作。知道不存在未排序的部分。时间复杂度为,因为每次都要线性扫描未排序的部分来找到最大值或者最小值。
直接选择排序是一种稳定排序。
1 | |
Heap Sort
The basic principle of Heap sort is from the data structure: Heap, where all nodes (or elements) are formed in order (ascending or descending). Heap maintain this properties, so every time you pop out the top element in the heap (or priority queue), it must be the biggest or the smallest element with highest priority in the queue.
For more information, you can search Binary Heap
We can use several ways to construct a heap (Binary heap, leftist heap, skew heap, binomial heap), the code demonstrated below shows the basic implementation of Binary Heap:
1 | |
当然,我们也可以直接使用STL中的堆来实现这一操作:
1 | |
注意自定义比较函数的设计!
可否优化?
在时间上,建堆的时间复杂度为,每一次出堆的时间复杂度为,因此总的时间复杂度为。
时间复杂度赏心悦目,但是引入了额外的空间开销:我们有的空间复杂度来维护一个堆。针对堆排序,我们是否可以借鉴堆的思想但是实现的空间复杂度呢?Of course you can!
为了实现空间复杂度的压缩,我们需要:
- 原地建堆。
- 随着堆元素的减少将被删除的元素append到元素的末尾。
有关具体的代码实现和二叉堆的实现非常类似(使用顺序存储满二叉树),我们将只会使用函数percolateDown()函数,在建树的时候正常对每一个非叶结点做过滤操作,然后在删除的时候我们并不是实质上的删除元素。(我们甚至都没有建立一个堆!)我们只是实现元素的交换顺序。
1 | |
复杂度分析
To be done.
使用决策树分析:根节点代表原始序列
则每一个叶子结点的序列都代表一个排序结果,也是一个排列!
关键证明:
Exchange Sort
交换排序的核心是逆序元素对的交换,例如如果我需要递增排序,那每一次交换操作可以表示为:
Bubble Sort
1 | |
Quick Sort
快速排序和冒泡排序类似,也是一种非常经典的选择排序的算法。但是时间复杂度更低,并且快速排序被认为是一种最快的内排序算法。
快速排序在相邻的内存中作比较!
Intuition:设置基准元素pivot。
因此快速排序的伪代码如下:
- 选择界点。
- 左右区间根据界点进行划分。
- 处理左右半段:
- 找到第一个大于界点的节点(从左到右遍历)
- 找到第一个小于界点的节点(从右向左遍历)
- 交换这两个元素
- 直到完全划分成左右两个部分。
然后对子数组进行递归实现即可。
How to choose pivot?
- 使用待排序元素的第一个元素作为标准元素。
- 最坏时间复杂度是平方级的
- 随机化快排
- 使用采样法取出中值。
代码实现
我们首先实现首元素为标准元素的快速排序算法,核心函数在于partition(即在取定划分之后处理左右两侧的情况),同时为了更方便的实现递归函数(分治法),我们使用包裹函数的设计:
1 | |
可以使用递推式证明在平均情况下,快速排序的时间复杂度为
随机化快排
更换了一种选择pivot的算法,因为选择首元素对于逆序数据的时间复杂度可以达到,因为不会有任何的交换发生。
1 | |
Merge Sort
归并排序的思想非常简单,给定,两个有序的数组,现在需要合并这两个数组并保持其有序性。因为,的有序性,只需要线性扫描一遍就可以实现。在快速排序中,使用了尾递归的方式由大化小,而在归并排序中也是类似,拆分至小数组并把小数组merge到大数组。
1 | |
Bucket Sort
基数排序的思想非常简单,例如在排序非负十进制整数的时候,按照个位数的取值把不同的数放在不同的口袋中,收集之后再倒出。
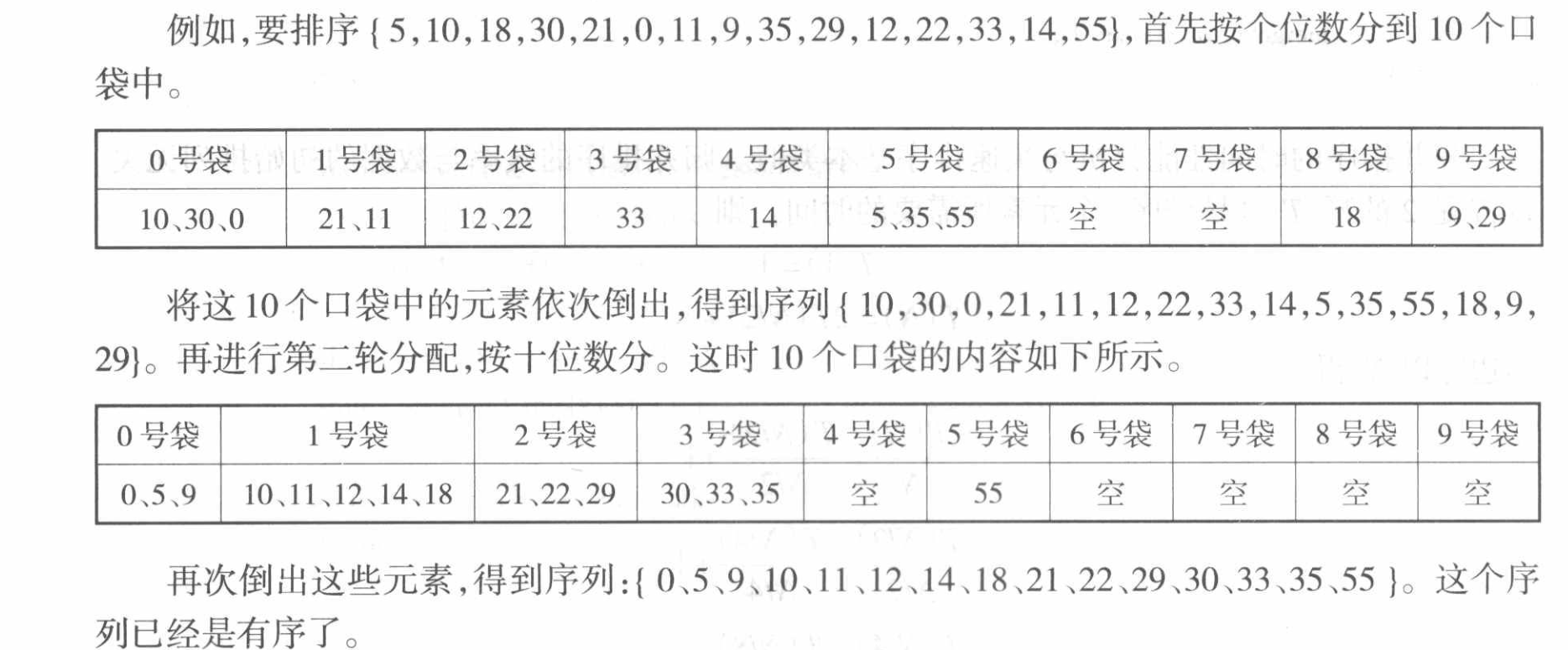
注意在上文的例子中,也可以先排十位数,只是需要注意在每个桶内的输入和输出的顺序要保持一致。
本质上和链表有点像!
1 | |
Sort in STL
在STL中已经实现了sort和stable_sort,使用非常的简单。
less and greater
在 C++ 标准模板库(STL)中,less 和 greater 是两个功能强大的比较函数对象(functor),它们主要用于排序和比较操作。以下是对这两个函数对象的详细介绍:
std::less
- 定义:
std::less是一个函数对象,用于判断左侧的值是否小于右侧的值。 - 用法:它可以用于 STL 中的容器(如
std::set、std::map)以及排序算法(如std::sort)。 - 示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {4, 2, 3, 1};
// 使用 std::less 进行排序
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::less<int>());
for (int num : vec) {
std::cout << num << " "; // 输出:1 2 3 4
}
return 0;
}
std::greater
- 定义:
std::greater是一个函数对象,用于判断左侧的值是否大于右侧的值。 - 用法:与
std::less类似,它也可以用于 STL 容器和排序操作,通常用于实现降序排序。 - 示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {4, 2, 3, 1};
// 使用 std::greater 进行降序排序
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::greater<int>());
for (int num : vec) {
std::cout << num << " "; // 输出:4 3 2 1
}
return 0;
}
All Codes
所有的排序算法的代码:
1 | |